Debug a Finding
CI Fuzz provides an intuitive way to debug a Finding.
This workflow applies to C/C++ projects with CMake as a build system.
The following fuzz test generates a Finding called exciting_eagle:
FUZZ_TEST(const uint8_t *data, size_t size) {
if(std::string((char*)data, size) != "crashing input") {
throw "Crash triggered";
}
}
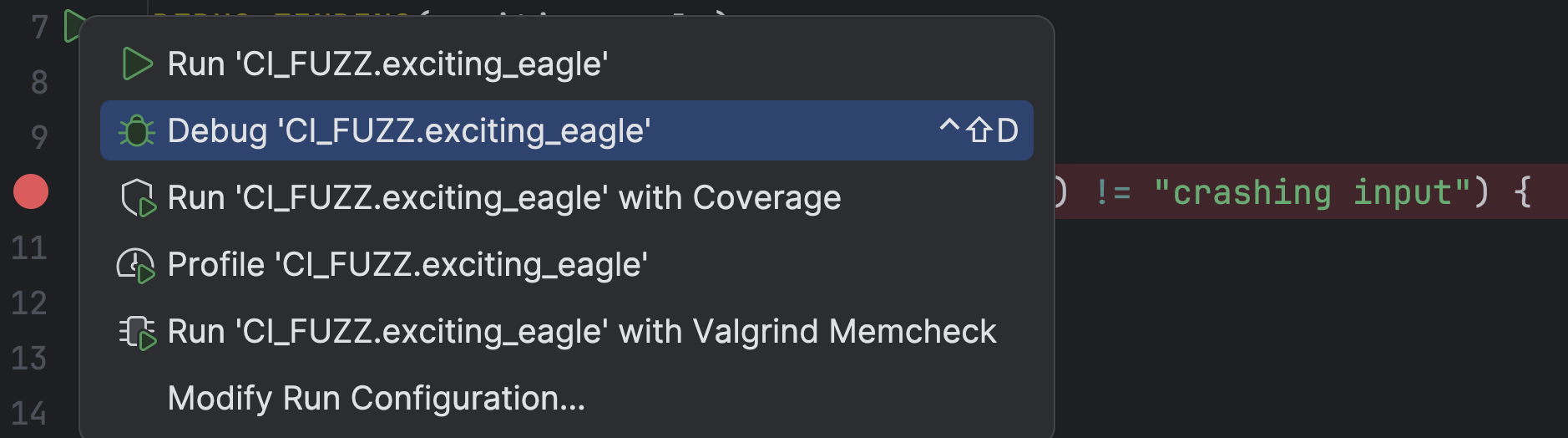
To debug this Finding, add the macro DEBUG_FINDING(...) to the source file containing the fuzz test.
This macro receives the name of the Finding as an argument:
DEBUG_FINDING(exciting_eagle)
FUZZ_TEST(const uint8_t *data, size_t size) {
if(std::string((char*)data, size) != "ci-daemon") {
throw "Crash triggered";
}
}
Furthermore, add the test framework of your choice to the fuzz test definition in the CMakeLists.txt file:
Currently CI Fuzz only supports Google Test.
add_fuzz_test(fuzz_test fuzz_test.cpp TEST_FRAMEWORK GTEST)
In case you didn't follow the default installation instructions of Google Test, it's possible to pass the target names of the Google Test libraries:
add_fuzz_test(fuzz_test fuzz_test.cpp TEST_FRAMEWORK GTEST TEST_FRAMEWORK_LIBS ${GTEST_BOTH_LIBRARIES})
You must instrument the fuzz test with the address sanitizer and undefined behavior sanitizer to reliably reproduce
Findings. Add the following lines to the top of the CMakeLists.txt before any commands related to the fuzz test:
add_compile_options(-fsanitize=address,undefined)
add_link_options(-fsanitize=address,undefined)
The IDE picks up the macro as a unit test, which in turn calls the fuzz test with the crashing input of the Finding:
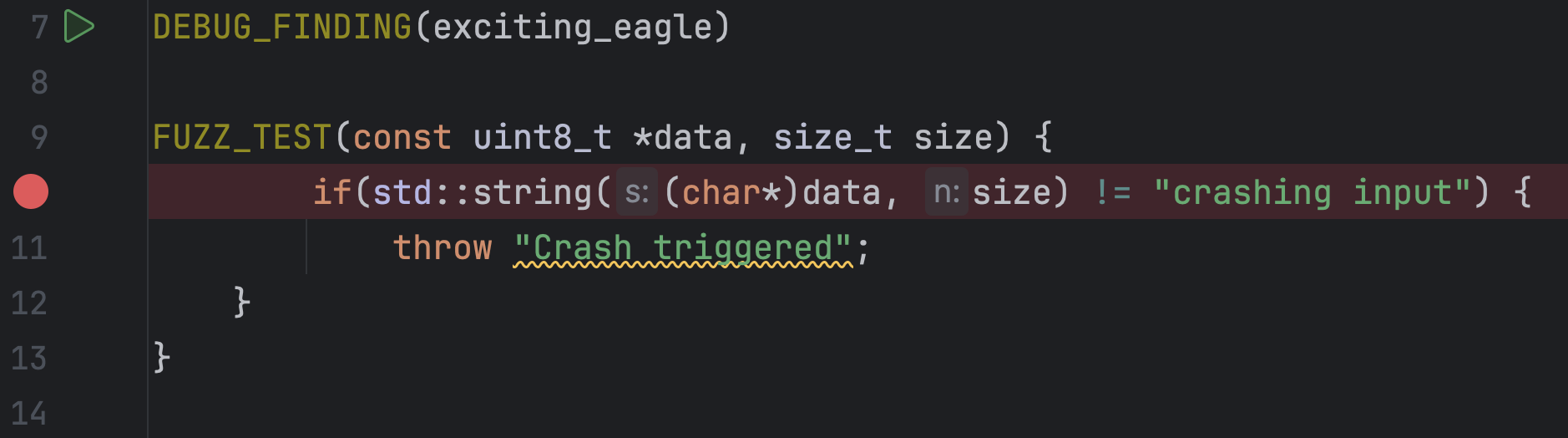
You can directly place a breakpoint in the fuzz test and debug the Finding: